
VC作为WEB程序的通用架构深受广大WEB程序员的拥护。 更是广泛成为面试题、考试试题、答辩问题等题材进行使用。
目前主流的语言框架及WEB系统大部分都是以MVC做为基础架构进行编写的。对于初学者而言理解MVC架构与熟悉业务逻辑的编写能极大的缩短学习一门语言框架的时间。然而初学者仅通过教材或许很难真正的理解MVC的架构及用法,在学习的过程中也可通过分析理解一些经典的语言框架进行学习。(例如:JSP + servlet + javabean)
初步认知
MVC模型:作为一种架构型的模式,无法直接实现功能添加,其主要作用是帮助我们对开发结构进行分层,使得代码结构更佳清晰合理化,将模型(model)、视图(view)、控制器(controller)进行分离。
将MVC通俗的理解可以想象成建筑一栋高楼大厦:
MVC:最终项目展示结果
模型(Model):建筑材料、建筑工具的集合(WEB项目中的数据模型及函数方法模型)
视图(View):建筑设计图纸、建筑展示效果图(WEB项目中数据的展示形态,优化丰富控制器传递过来的数据并进行展示)
控制器(Controller):建筑工程师、施工人员(WEB项目中通过调取对应数据模型及函数方法模型产生数据并传递给相关视图层)
施工人员(Controller)通过使用建筑工具(Model)将建筑材料(Model)按着设计图纸(View)进行搭建填装,最后组装成一栋高楼大厦。
深入理解
模型(Model):模型层的重点在于模块化,重点思路在于将可复用可集成的代码封装成函数方法集成在模型层中方便复用及代码维护。(例如:用户登录验证,这段代码可能在多个不同的控制器中都需要使用,若将其封装成方法写入模型层,则控制器如果有需求只需导入对应的模型层并以传参的方式进行调用既可省去大量重复代码,并且在进行维护的时候也仅需对模型层中的封装方法进行修改就能实现全局维护)
视图(View):视图层的重点在于数据展示,视图层的框架要便于数据展示,避免大量逻辑代码的存在,尽量通过简单的循环语句将控制层获取的数据进行展示,所以的数据处理应尽量于控制层与模型层实现。(当然视图层也可以适当使用模块化的设计思路,例如:标准WEB网站中,大量网页头部及尾部代码都是重复的,这些重复视图层代码可以通过MVC模式的思路封装到一个单独的HTML页面,在需要时通过相关语句载入对应的页面中,可以大量减少重复代码。)
控制器(Controller):控制层主要做为模型层与视图层的控制中枢。控制器应避免重复视图层与模型层的工作,将数据的展示封装至模型层,可复用的数据获取与数据逻辑处理则在模型层中封装成函数方法。控制层应做到精简。
学编程技术,就到W3Cschool,如果你喜欢我们的文章,可以点击右上角关注我们;如果你想看到更多IT界的资讯,可以加我们的公众号。
公众号:w3cschoolcn
言
学了一遍SpringMVC以后,想着做一个总结,复习一下。复习写下面的总结的时候才发现,其实自己学得并不彻底、牢固、也没有学全,视频跟书本是要结合起来一起,每一位老师的视频可能提到的东西都不一致,也导致也不是很全面,书本上会讲的笔记系统、全面。同时我自己也是一个初学者,下面总结的可能并不完善、正确,希望看到的大神给我指出,在此非常感谢。
目录
Spring Web MVC (下文简称为 SpringMVC )是 Spring 提供 Web 应用的框架设计,属于表现层的框架。SpringMVC是Spring框架的一部分。
Spring框架包括大致六大模块,核心容器(Core Container)、AOP和设备支持、数据访问及集成、Web、报文发送、Test
图片来源于Spring官网5.0.0.M5:
? https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.0.0.M5/spring-framework-reference/html/overview.html#overview-modules
对于Spring5模块图,有2点疑问:
1、不清楚为什么在Spring官网上5.0版本以后,Release版(稳定版)的都未找到模块图,但是在M(里程碑版)版找到 了,如果有人在5.0以后的Release版(稳定版)找到,麻烦给我留个言,谢谢。
2、在其他博文中看到Spring5模块结构图是这样的:
挺奇怪这个图是哪里来的?(路过的大神请指点)
对于问题2,我在Spring5.2.13.RELEASE GA中,找到了如下所示信息:
拷贝以上信息:
Spring Framework Documentation
Version 5.2.13.RELEASE
What’s New, Upgrade Notes, Supported Versions, and other topics, independent of release cadence, are maintained externally on the project’s Github Wiki.
Overview | history, design philosophy, feedback, getting started. |
Core | IoC Container, Events, Resources, i18n, Validation, Data Binding, Type Conversion, SpEL, AOP. |
Testing | Mock Objects, TestContext Framework, Spring MVC Test, WebTestClient. |
Data Access | Transactions, DAO Support, JDBC, O/R Mapping, XML Marshalling. |
Web Servlet | Spring MVC, WebSocket, SockJS, STOMP Messaging. |
Web Reactive | Spring WebFlux, WebClient, WebSocket. |
Integration | Remoting, JMS, JCA, JMX, Email, Tasks, Scheduling, Caching. |
Languages | Kotlin, Groovy, Dynamic Languages. |
按照以上信息的Web Servlet、Web Reactive已经是分属于不同的模块了。
Spring官方文档:https://spring.io/projects/spring-framework#learn/
上面提到了Spring有不同的版本,在此记录一下各个版本的意义。
描述方式 | 说明 | 含义 |
Snapshot | 快照版 | 尚不稳定,仍处于开发中的版本 |
Release | 稳定版 | 功能相对稳定,可以对外发行,但有时间限制 |
GA | 正式版 | 代表广泛可用的稳定版(General Availability) |
M | 里程碑版 | (M是Milestone的意思)具有一些全新的功能或是有意义的版本 |
RC | 终测版 | Release Candidate(最终测试),即将作为正式版发布 |
SpringMVC执行流程图
图片来源:三、引用参考资料
(1) 处理器映射器:springmvc框架中的一种对象,框架把实现了HandlerMapping接口的类都叫做映射器(多个);
(2) 处理器映射器作用:根据请求,从springmvc容器对象中获取处理器对象(MyController controller=ctx.getBean("some")
(3) 框架把找到的处理器对象放到一个叫做处理器执行链(HandlerExecutionChain)的类保存
(4) HandlerExecutionchain:类中保存着
?a:处理器对象(MyController);
?b:项目中的所有的拦截器List
(5) 方法调用:HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler - getHandler (processedRequest);
(1) HandlerExecutionChain执行链找到对应的处理器映射器HandlerAdapter。
(2) 处理器适配器:springmvc框架中的对象,需要实现HandlerAdapter接口,
(3) 处理器适配器作用:执行处理器方法(调用MyController.doSome()得到返回值ModelAndView )
(4) 前端控制器中调用适配器:HandlerAdapter ha=getHandlerAdapter (mappedHandler.getHandler());
(5) 执行处理器方法:mv=ha.handle (processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
第08说明:
(1) 视图解析器:springmvc中的对象,需要实现ViewResoler接口(可以有多个)
(2) 视图解析器作用:组成视图完整路径,使用前缀,后缀。并创建View对象。
(3) view是一个接口,表示视图的,在框架中jsp,htm1不是string表示,而是使用view和他的实现类表示视图。
InternalResourceview:视图类,表示jsp文件,视图解析器会创建InternalResourceView类对象。 这个对象的里面,有一个属性url-/WEB-INF/view/show.jsp
综上所述,总结下SpringMVC的详细流程图:
图片来源:三、引用参考资料
以下源码来源jar包:spring-webmvc-5.25.RELEASE.jar
? ApplicationContext初始化入口类:ApplicationObjectSupport的setApplicationContext方法,setApplicationContext方法中核心部分就是初始化容器initApplicationContext(context),子类AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping实现了该方法。
类图:
UML图:
? RequestMappingHandlerMapping ,用于注解@Controller,@RequestMapping来定义controller.
初始化时,3个类的大致分工如下:
? 从上面的流程图可以看到前端控制器(中央处理器)DistepcherServlet是SpringMVC核心,查看DistepcherServlet类的继承情况。
UML图:
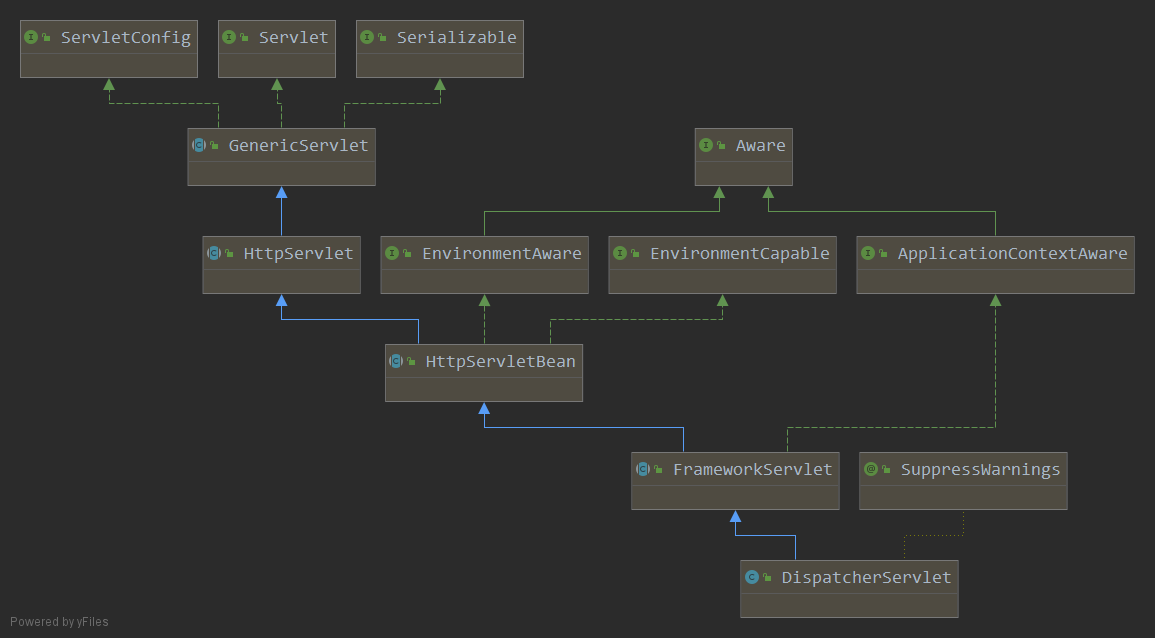
从继承关系看出:
? DistepcherServlet ---> FrameworkServlet ---> HttpServletBean---> HttpServlet
? 那就说明DistepcherServlet 类也是一个Servlet类,那最终核心的方法就是service()方法,即Servlet的核心方法。
? 那就找service()方法,在DistepcherServlet中没有servic()方法,在父类FrameworkServlet有service()方法,源码如下:
来源:
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
/**
* Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH requests.
*/
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod=HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod==HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod==null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
可以看到:
FrameworkServlet.service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)拿到request请求,判断当前请求是否是PATCH请求,不是的就调用父类的servic()方法,调用父类中的service方法就是去调用该类中doPost(),doGet()方法,根据不同的请求方式然后走doPost()或者doGet(),调用中以doGet()为例,
FrameworkServlet类的doGet()源码:
/**
* Delegate GET requests to processRequest/doService.
* <p>Will also be invoked by HttpServlet's default implementation of {@code doHead},
* with a {@code NoBodyResponse} that just captures the content length.
* @see #doService
* @see #doHead
*/
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
? doGet()又调用FrameworkServlet类中的processRequest(request, response);
/**
* Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome.
* <p>The actual event handling is performed by the abstract
* {@link #doService} template method.
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause=null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext=LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext=buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes=RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes=buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager=WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause=ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause=ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes !=null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
? processRequest(request, response)方法中最关键的又调用了doService(request, response);查看FrameworkServlet类中的doService(request, response),或者是调试跟踪可知,doService(request, response)由子类DispatcherServlet实现。
源码来源:
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
/**
* Subclasses must implement this method to do the work of request handling,
* receiving a centralized callback for GET, POST, PUT and DELETE.
* <p>The contract is essentially the same as that for the commonly overridden
* {@code doGet} or {@code doPost} methods of HttpServlet.
* <p>This class intercepts calls to ensure that exception handling and
* event publication takes place.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
* @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doGet
* @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doPost
*/
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;
? 查看DispatcherServlet中的doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)方法
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch}
* for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot=null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot=new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames=request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName=(String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager !=null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap=this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap !=null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot !=null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
? DispatcherServlet的doService()方法中最终调用doDispatch(request, response),查看源码如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch()
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest=request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler=null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed=false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager=WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv=null;
Exception dispatchException=null;
try {
// 文件上传相关,判断是不是二进制请求
processedRequest=checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed=(processedRequest !=request);
// 取得处理当前请求的controller,这里也称为hanlder处理器,第一个步骤的意义就在这里体现了.这里并不是直接返回controller,而是返回的HandlerExecutionChain请求处理器链对象,该对象封装了handler和拦截器interceptors.
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler=getHandler(processedRequest);
// 如果handler为空,则返回404
if (mappedHandler==null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//3. 获取处理request的处理器适配器HandlerAdapter
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha=getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method=request.getMethod();
boolean isGet="GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified=ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//处理器适配器执行之前,检查拦截器的方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//处理器适配器根据找到,执行handler,返回ModelAndView
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv=ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException=ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException=new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler !=null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
? 可以看出doDispatch()就是SpringMVC的核心代码了,分析doDispatch():
? 首先看下处理器映射器HandlerMapping类图:
doDispatch()关键代码:
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler=null;
mappedHandler=getHandler(processedRequest);
? mappedHandler是一个执行链HandlerExecutionChain 对象,这里封装了handler和拦截器interceptors,getHandler(processedRequest)方法就是从处理器映射器HandlerMapping中找到url和controller的对应关系,并返回给前端控制器DispatchServlet。
查看getHandler(processedRequest);源码:
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings !=null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler=mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler !=null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
调试代码如下:
从代码调试中可以看到handlerMapping中有三个对象:
this.handlerMappings={ArrayList@4662} size=3
0={BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping@4791}
1={RequestMappingHandlerMapping@4792}
2={RouterFunctionMapping@4793}
接着看getHandler(HttpServletRequest request)方法,先遍历HandlerMappers,查找控制器找到之后就返回执行链HandlerExecutionChain类型的Handler。
可以看到返回的Handler中,拿到的就是我们自己编码的Controller类,以及拦截器(演示项目中未编写,所以调试汇总返回的Handler最后是0 interceptors)
HandlerExecutionChain with [com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController#doSome()] and 0 interceptors
将正在调试的idea打开自己编写的Controller来对照,发现一致:
doDispatch()里面的关键代码:
HandlerAdapter ha=getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
源码如下:
/**
* Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object.
* @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for
* @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error.
*/
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters !=null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
为什么还要获取处理器适配器HandlerAdapter:与获取处理器映射器HandlerMapping一样,Spring提供了不通的处理器适配器。
调试如下:
查看DEBUG调试模式中getHandlerAdapter()方法在中的:
handler、adapter、this.handlerAdapters
以下是拷贝的结果:
handler
handler={HandlerMethod@4792} "com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController#doSome()"
logger={LogAdapter$JavaUtilLog@4858}
bean={MyController@4859}
beanFactory={DefaultListableBeanFactory@4847} "org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@56b5a4c3: defining beans [myController,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory,org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver#0]; root of factory hierarchy"
beanType={Class@3782} "class com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController"
method={Method@4860} "public org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController.doSome()"
bridgedMethod={Method@4860} "public org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController.doSome()"
parameters={MethodParameter[0]@4861}
responseStatus=null
responseStatusReason=null
resolvedFromHandlerMethod={HandlerMethod@4863} "com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController#doSome()"
interfaceParameterAnnotations=null
description="com.bjpowernode.controller.MyController#doSome()"
adapter
adapter={RequestMappingHandlerAdapter@4827}
customArgumentResolvers=null
argumentResolvers={HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite@4833}
initBinderArgumentResolvers={HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite@4834}
customReturnValueHandlers=null
returnValueHandlers={HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite@4835}
modelAndViewResolvers=null
contentNegotiationManager={ContentNegotiationManager@4836}
messageConverters={ArrayList@4837} size=4
requestResponseBodyAdvice={ArrayList@4838} size=0
webBindingInitializer=null
taskExecutor={SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor@4839}
asyncRequestTimeout=null
callableInterceptors={CallableProcessingInterceptor[0]@4840}
deferredResultInterceptors={DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor[0]@4842}
reactiveAdapterRegistry={ReactiveAdapterRegistry@4844}
ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect=false
cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers=0
synchronizeOnSession=false
sessionAttributeStore={DefaultSessionAttributeStore@4845}
parameterNameDiscoverer={DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer@4846}
beanFactory={DefaultListableBeanFactory@4847} "org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@56b5a4c3: defining beans [myController,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory,org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver#0]; root of factory hierarchy"
sessionAttributesHandlerCache={ConcurrentHashMap@4848} size=0
initBinderCache={ConcurrentHashMap@4849} size=0
initBinderAdviceCache={LinkedHashMap@4850} size=0
modelAttributeCache={ConcurrentHashMap@4851} size=0
modelAttributeAdviceCache={LinkedHashMap@4852} size=0
order=2147483647
supportedMethods=null
allowHeader="GET,HEAD,POST,PUT,PATCH,DELETE,OPTIONS"
requireSession=false
cacheControl=null
cacheSeconds=-1
varyByRequestHeaders=null
useExpiresHeader=false
useCacheControlHeader=true
useCacheControlNoStore=true
alwaysMustRevalidate=false
servletContext={ApplicationContextFacade@4754}
logger={LogAdapter$JavaUtilLog@4854}
applicationContext={XmlWebApplicationContext@4665} "WebApplicationContext for namespace 'myweb-servlet', started on Tue Mar 02 23:25:35 CST 2021"
messageSourceAccessor={MessageSourceAccessor@4855}
this.handlerAdapters
this.handlerAdapters={ArrayList@4658} size=4
0={HttpRequestHandlerAdapter@4810}
1={SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter@4820} //XML方式
2={RequestMappingHandlerAdapter@4827} //注解方式
3={HandlerFunctionAdapter@4832}
可以看到找到4个处理器适配器。通过DEBUG模式可以看到,此次取到的处理器适配器HandlerAdapter是:RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
ha={RequestMappingHandlerAdapter@4827}
doDispatch()中的关键代码:
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExecutionChain#applyPreHandle
applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)源码:
/**
* Apply preHandle methods of registered interceptors.
* @return {@code true} if the execution chain should proceed with the
* next interceptor or the handler itself. Else, DispatcherServlet assumes
* that this interceptor has already dealt with the response itself.
*/
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors=getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i=0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor=interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex=i;
}
}
return true;
}
doDispatch()中的关键代码:
mv=ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
DEBUG模式调试,是调到了:
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#handle
源码如下:
/**
* This implementation expects the handler to be an {@link HandlerMethod}.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
再往下看handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler)方法,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#handleInternal
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session=request.getSession(false);
if (session !=null) {
Object mutex=WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav=invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav=invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav=invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
注意,handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler)方法的返回值是ModelAndView ,这里就完成了处理器适配器HandlerAdapter执行Handler(Controller)并将结果ModelAndView返回给前端控制器DistepchServlet
??接上2.3:前端控制器DistepchServlet接收到处理器适配器HandlerAdapter返回的ModelAndView以后,这里分2种情况:
总结一下:
视图解析器ViewResolver接口主要作用是解析前端控制器DispatcherServlet传递的逻辑视图名,并将解析结果的真正的视图对象View传回给前端控制器DispatcherServlet
ViewResolverd的实现类:
ViewResolver的UML:
.png)
视图类型 | 简介 | |
URL视图资源图 | InternalResourceView | 将JSP或其他资源封装成一个视图。被视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver默认使用。 |
JstlView | InternalResourceView的子类。如果JSP中使用了JSTL的国际化标签,就需要使用该视图类。 | |
文档视图 | AbstractExcelView | Excel文档视图的抽象类。 |
AbstractPdfView | PDF文档视图的抽象类 | |
报表视图 | ConfigurableJasperReportsView | 常用的JasperReports报表视图 |
JasperReportsHtmlView | ||
JasperReportsPdfView | ||
JasperReportsXlsView | ||
JSON视图 | MappingJackson2JsonView | 将数据通过Jackson框架的ObjectMapper对象,以JSON方式输出 |
DispatcherServlet.properties文件是在SpringMVC架包中:
DispatcherServlet.properties内容:
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
SpringMVC为什么能加载不同处理器映射器HandlerMapping、处理器适配器handlerAdapter,就是因为框架配置了这个DispatcherServlet.properties文件。
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/chuchq/p/14489716.html
VC作为WEB程序的通用架构深受广大WEB程序员的拥护。 更是广泛成为面试题、考试试题、答辩问题等题材进行使用。
目前主流的语言框架及WEB系统大部分都是以MVC做为基础架构进行编写的。对于初学者而言理解MVC架构与熟悉业务逻辑的编写能极大的缩短学习一门语言框架的时间。然而初学者仅通过教材或许很难真正的理解MVC的架构及用法,在学习的过程中也可通过分析理解一些经典的语言框架进行学习。(例如:JSP + servlet + javabean)
初步认知
MVC模型:作为一种架构型的模式,无法直接实现功能添加,其主要作用是帮助我们对开发结构进行分层,使得代码结构更佳清晰合理化,将模型(model)、视图(view)、控制器(controller)进行分离。
将MVC通俗的理解可以想象成建筑一栋高楼大厦:
MVC:最终项目展示结果
模型(Model):建筑材料、建筑工具的集合(WEB项目中的数据模型及函数方法模型)
视图(View):建筑设计图纸、建筑展示效果图(WEB项目中数据的展示形态,优化丰富控制器传递过来的数据并进行展示)
控制器(Controller):建筑工程师、施工人员(WEB项目中通过调取对应数据模型及函数方法模型产生数据并传递给相关视图层)
施工人员(Controller)通过使用建筑工具(Model)将建筑材料(Model)按着设计图纸(View)进行搭建填装,最后组装成一栋高楼大厦。
深入理解
模型(Model):模型层的重点在于模块化,重点思路在于将可复用可集成的代码封装成函数方法集成在模型层中方便复用及代码维护。(例如:用户登录验证,这段代码可能在多个不同的控制器中都需要使用,若将其封装成方法写入模型层,则控制器如果有需求只需导入对应的模型层并以传参的方式进行调用既可省去大量重复代码,并且在进行维护的时候也仅需对模型层中的封装方法进行修改就能实现全局维护)
视图(View):视图层的重点在于数据展示,视图层的框架要便于数据展示,避免大量逻辑代码的存在,尽量通过简单的循环语句将控制层获取的数据进行展示,所以的数据处理应尽量于控制层与模型层实现。(当然视图层也可以适当使用模块化的设计思路,例如:标准WEB网站中,大量网页头部及尾部代码都是重复的,这些重复视图层代码可以通过MVC模式的思路封装到一个单独的HTML页面,在需要时通过相关语句载入对应的页面中,可以大量减少重复代码。)
控制器(Controller):控制层主要做为模型层与视图层的控制中枢。控制器应避免重复视图层与模型层的工作,将数据的展示封装至模型层,可复用的数据获取与数据逻辑处理则在模型层中封装成函数方法。控制层应做到精简。
学编程技术,就到W3Cschool,如果你喜欢我们的文章,可以点击右上角关注我们;如果你想看到更多IT界的资讯,可以加我们的公众号。
公众号:w3cschoolcn
*请认真填写需求信息,我们会在24小时内与您取得联系。